Blog Details
AI Agents vs. AI Assistants – Which One Does Your Business Need?
As artificial intelligence becomes more common in everyday business and personal applications, terms like AI agents and AI assistants are often used interchangeably. However, there are key differences between the two, especially in how they operate, the level of autonomy they possess, and the roles they fulfil.
Understanding these differences is important for businesses and individuals looking to adopt the right AI solution for their needs. Let’s explore what sets AI agents apart from AI assistants in simple terms.
1. Definitions and Core Concepts
![definitions-and-core-concepts-min[1].jpg](/media/qx2cmnso/definitions-and-core-concepts-min-1.jpg)
AI Assistants
At its core, an AI assistant is designed to aid users in performing specific tasks or providing information upon request. Think of them as digital helpers that respond to direct commands or queries. They are typically reactive, meaning they wait for user input to initiate an action. Examples include virtual assistants like Siri, Alexa, and Google Assistant, as well as AI-powered chatbots for customer service or personal productivity tools that help with tasks like scheduling, email management, or content generation..
Key characteristics:
-
User-driven interaction
-
Task-oriented (e.g., scheduling, searching, reminders)
-
Often integrated into smartphones, smart speakers, and productivity tools
Examples:
-
Apple Siri
-
Google Assistant
-
Amazon Alexa
-
Microsoft Cortana
How AI Assistants Work
AI assistants rely on user prompts. You ask them a question or tell them what to do, and they respond accordingly. They typically perform actions such as:
-
Setting reminders or alarms
-
Sending messages
-
Answering questions
-
Providing recommendations
-
Booking appointments
They work reactively — meaning they wait for input and then respond.
AI Agents
An AI agent, on the other hand, is a more sophisticated and autonomous entity. It is designed to perceive its environment, make decisions, and take actions to achieve specific goals without constant explicit instructions from a user. AI agents can proactively identify problems, plan solutions, and execute tasks independently. They often possess learning capabilities, allowing them to adapt and improve their performance over time based on experience and data. Examples range from self-driving cars that navigate complex environments to AI systems used in financial trading that can execute trades based on market analysis.
Key characteristics:
-
Goal-driven autonomy
-
Can sense, reason, and act in dynamic environments
-
May communicate with other agents or systems
Examples:
-
Self-driving car navigation systems
-
Automated trading bots in finance
-
Multi-agent systems in logistics or robotics
-
Game-playing agents (e.g., AlphaGo, OpenAI Five)
How AI Agents Work
AI agents function autonomously and may use machine learning, goal-setting algorithms, or reasoning engines to make decisions. They:
-
Understand context and objectives
-
Set sub-goals and plans
-
Act independently in dynamic environments
-
Learn and improve over time
For example, instead of waiting for you to ask, an AI agent might detect a drop in sales and automatically trigger a campaign or alert the marketing team.
2. Technical Architecture
AI Assistant Architecture
-
Input Processing: Uses speech recognition or text parsing to understand user commands.
-
Natural Language Understanding (NLU): Interprets user intent and extracts relevant information.
-
Task Execution: Maps intent to predefined actions (e.g., sending a message, fetching weather).
-
Response Generation: Provides feedback or results to the user in natural language.
Most assistants rely on cloud-based AI models, rule-based logic, and integration with third-party services.
AI Agent Architecture
-
Perception: Uses sensors, data feeds, or APIs to observe the environment.
-
Decision-Making: Employs AI planning, reasoning, or learning algorithms to choose actions.
-
Action: Executes actions that affect the environment or other agents.
-
Learning: Continuously adapts using feedback, reinforcement learning, or experience replay.
Agents may operate in distributed, multi-agent environments and often require robust frameworks for coordination and negotiation.
3. Autonomy and Proactivity
Autonomy: This is perhaps the most significant distinction.
-
AI Assistants: Exhibit low autonomy. They primarily operate under direct user command. They can perform tasks, but the initiation and often the step-by-step guidance come from the user. While they can use tools and perform predefined functions, they typically cannot independently decide on goals or how to achieve them without a prompt.
-
AI Agents: Possess high autonomy. Once given a goal, they can independently plan, decide on the necessary steps, and execute them. They can interact with their environment, utilize tools, and even collaborate with other agents to achieve their objectives with minimal human intervention.
Proactiveness vs. Reactiveness:
-
AI Assistants: Are largely reactive. They wait for a trigger, usually a user request, to perform an action or provide information.
-
AI Agents: Can be proactive. They can monitor their environment, identify opportunities or problems, and initiate actions without a direct user prompt to achieve their assigned goals.
|
Aspect |
AI Assistants |
AI Agents |
|
Initiative |
Reactive: Waits for user input |
Proactive: Can initiate actions |
|
Autonomy Level |
Low to moderate |
High (can operate independently) |
|
Adaptation |
Limited personalization |
Learns and adapts to changing scenarios |
Example: A smart home assistant will turn off the lights when asked. An AI agent might monitor energy usage, predict occupancy patterns, and autonomously manage lighting and climate control for efficiency.
4. Task Complexity and Scope
AI Assistants: Are generally suited for simpler, well-defined tasks, such as setting reminders, answering factual questions, generating basic content, or controlling smart home devices.
-
AI Assistants are best for routine, well-defined tasks:
-
Setting alarms
-
Sending texts
-
Answering FAQs
-
Providing directions
AI Agents: Are designed to handle more complex tasks and workflows that may involve multiple steps, decision-making, and interaction with various systems or environments. They can analyze large datasets, predict trends, and execute multi-stage processes autonomously.
-
AI Agents excel in complex, multi-step, or dynamic tasks:
-
Managing supply chains
-
Autonomous vehicle navigation
-
Automated negotiation in e-commerce
-
Multi-robot coordination in manufacturing
5. Learning and Adaptation
![learning-and-adaptation-min[1].jpg](/media/zqefe5gr/learning-and-adaptation-min-1.jpg)
AI Assistants: May have some learning capabilities to improve user interaction or personalize responses based on past interactions. However, their learning is often limited to enhancing user experience within a defined scope. Significant updates and new capabilities usually require developer intervention.
-
-
May use machine learning for voice recognition or intent classification
-
Personalization is often shallow (e.g., remembering preferences)
-
AI Agents: Frequently employ machine learning algorithms to continuously learn from their environment, adapt their strategies, and improve their performance over time. This allows them to handle new situations effectively and optimize their actions based on experience.
-
-
Employ advanced learning (reinforcement, deep learning)
-
Can optimize strategies, discover new solutions, and generalize from experience
-
May collaborate or compete with other agents, leading to emergent behaviors
-
6. Interaction and Communication
AI Assistants: Typically feature user-friendly interfaces designed for direct interaction through voice commands, text inputs, or graphical interfaces. The focus is on ease of use and accessibility for everyday tasks.
-
-
Primarily interact with humans
-
Use natural language (text/voice) interfaces
-
Focused on user experience and convenience
-
AI Agents: May or may not have a direct user interface. Many operate in the background, integrated into broader systems or applications, focusing on autonomous decision-making and task execution rather than direct user engagement.
-
-
May interact with humans, other agents, or external systems
-
Use structured protocols, APIs, or agent communication languages
-
Can form multi-agent systems for distributed problem-solving
-
7. Real-World Applications
AI Assistant Use Cases
-
Personal productivity (calendars, reminders)
-
Smart home control (lights, thermostats)
-
Customer service chatbots
-
Hands-free device operation
AI Agent Use Cases
-
Autonomous vehicles (navigation, obstacle avoidance)
-
Financial trading bots (real-time market analysis)
-
Industrial automation (robotic assembly lines)
-
Distributed energy grid management
-
Game AI (strategy, real-time adaptation)
9. Future Trends
-
Convergence: The line between assistants and agents is blurring. Next-generation AI assistants may incorporate agent-like autonomy, while agents may gain more natural, human-like interfaces.
-
Multi-Agent Systems: The future will see more collaborative AI agents, working together or with humans in complex ecosystems (e.g., smart cities, autonomous supply chains).
-
Personalization and Context Awareness: Both assistants and agents will become more contextually aware and capable of personalized, adaptive behavior.
10. Summary Table
|
Feature |
AI Assistants |
AI Agents |
|
Primary Role |
User helper |
Autonomous problem solver |
|
Interaction |
Conversational, user-facing |
System-facing, may interact with agents |
|
Autonomy |
Low to moderate |
High |
|
Learning |
Limited, user-focused |
Advanced, environment-focused |
|
Task Complexity |
Simple, routine |
Complex, dynamic |
|
Examples |
Siri, Alexa, chatbots |
Self-driving cars, trading bots |
Examples to Illustrate the Difference
-
Asking Siri for the weather forecast is an interaction with an AI Assistant. It reacts to your query and provides the requested information.
-
A self-driving car using sensor data to navigate traffic, make decisions about speed and lane changes, and reach a destination without constant human control is an example of an AI Agent. It perceives its environment and acts autonomously to achieve the goal of transportation.
-
A customer service chatbot that answers frequently asked questions is an AI Assistant.
-
An AI system in a call center that can proactively identify customer issues, access relevant information, and autonomously offer solutions or escalate complex problems is functioning as an AI Agent.
-
Using ChatGPT to draft an email is leveraging an AI Assistant for content generation.
-
An AI-powered marketing platform that analyzes market trends, predicts customer behavior, and autonomously adjusts advertising campaigns to optimize results acts as an AI Agent.
Overlap and Evolution
It's important to note that the line between AI Agents and AI Assistants can sometimes blur, and the field is continuously evolving. Some advanced AI assistants are incorporating more autonomous features, taking proactive steps based on user patterns or contextual information. Conversely, AI agents may have user interfaces for monitoring or providing high-level instructions.
Furthermore, the development of multi-agent systems, where multiple AI agents collaborate or compete to achieve a common goal, represents a significant advancement in the capabilities of AI agents, allowing them to tackle even more complex challenges
Why This Matters for Businesses
The difference between AI assistants and agents matters when choosing the right technology for your business:
-
AI Assistants are great for basic automation, like setting reminders, answering FAQs, or scheduling meetings.
-
AI Agents are ideal for intelligent automation, such as managing customer conversations, analyzing data, and taking action to improve sales or support without human input.
If your goal is to boost productivity or streamline workflows, an AI assistant might be enough. But if you want your AI to act, learn, and make decisions, then an AI agent is the better choice.
Conclusion
AI assistants and AI agents represent two distinct paradigms in artificial intelligence. Assistants are designed to make our lives easier through responsive, user-driven interactions. Agents, on the other hand, are built for autonomy, adaptability, and complex problem-solving, often operating behind the scenes or in tandem with other agents.
As AI technology matures, the distinctions may blur, but understanding these differences is essential for developers, businesses, and users looking to harness the right AI for their needs. Whether you need a helpful digital companion or a robust autonomous system, the choice between AI assistants and AI agents will shape the future of your intelligent solutions.
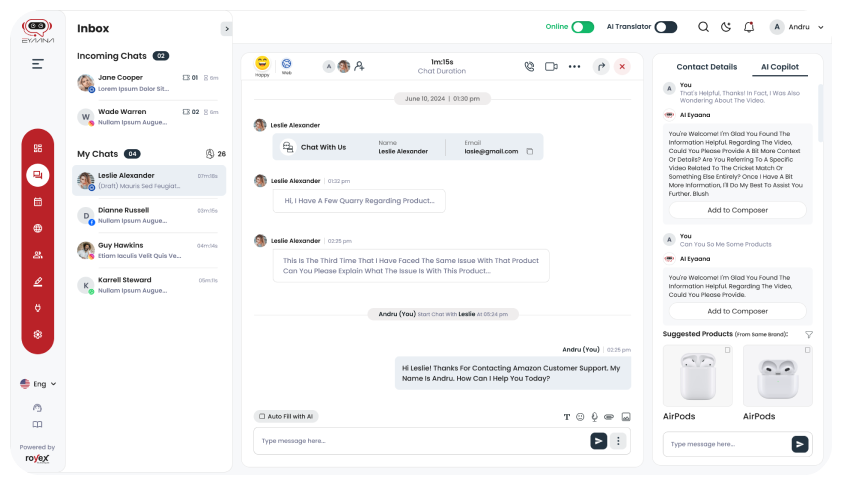
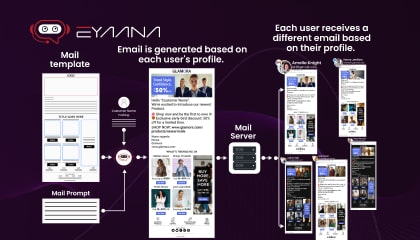
Why Eyaana is the Best Choice for AI Chatbot?
![why-eyaana-is-the-best-choice-min[1].jpg](/media/iz0dvyta/why-eyaana-is-the-best-choice-min-1.jpg)
If you’re looking for a powerful yet user-friendly AI chatbot app, Eyaana, customer service ai is worth considering. With Eyaana, businesses can seamlessly turn website traffic into live, engaging conversations, making it easier to convert leads into customers.
Eyaana is designed to be an AI-first customer support and sales solution, meaning it comes with powerful automation features, yet it’s easy to use even for non-technical teams. Its inbuilt CRM and helpdesk make customer management simple, while its AI-driven chat capabilities provide a smart, personalized experience for users.
Inbuilt CRM and Helpdesk: Eyaana comes with a built-in CRM and helpdesk, allowing businesses to manage customer data and support interactions in one place.
Flexible Pricing: Choose from Eyaana’s Lite and Pro packages starting from $99/month, with flexible, commitment-free tiers tailored to suit businesses of all sizes.
Multilingual Support: Engage a diverse audience with language options like Arabic, English, Hindi, and Urdu.
AI-First Design: Eyaana’s chatbot learns over time, enhancing customer interactions and turning site visits into conversations.
Scalability: Eyaana adapts to business growth, handling higher customer interactions with ease.
24/7 Support & Analytics: Real-time data and round-the-clock support help improve customer experiences.
For businesses looking to implement 24/7 customer support, Eyaana offers an excellent solution. With advanced AI capabilities, Eyaana is designed to provide fast, accurate, and personalized customer service around the clock. By choosing Eyaana, businesses can ensure that their customers are always taken care of, without needing to rely on human agents for every single inquiry. Whether it’s for answering questions, troubleshooting issues, or processing orders, Eyaana can help businesses deliver seamless 24/7 support with ease.
To explore how AI can enhance your business operations, sign up for free and get started with Eyaana today.
Do you need help?
We will provide detailed information about our services, types of work, and top projects. We will calculate the cost and prepare a commercial proposal.